Become a Patron!
True Information is the most valuable resource and we ask you to give back.

Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures Used in the 22 March 2016 Brussels Attacks
Page Count: 9 pages
Date: April 12, 2016
Restriction: For Official Use Only
Originating Organization: Department of Homeland Security, Federal Bureau of Investigation, National Counterterrorism Center
File Type: pdf
File Size: 254,019 bytes
File Hash (SHA-256): 5840AF768DA275DAA059648BFFF85B2E314544AA07F275459392D11BD4CF6602
Download File
(U//FOUO) This Joint Intelligence Bulletin (JIB) is intended to provide a review of the tactics, techniques, and procedures demonstrated by the perpetrators of the 22 March 2016 attacks in Brussels, Belgium. The analysis in this JIB is based on statements by European government and law enforcement officials cited in media reporting and is subject to change with the release of official details from post-incident investigations. This JIB is provided by DHS, FBI, and NCTC to support their respective activities and to assist federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government counterterrorism and law enforcement officials, first responders and private sector partners in deterring, preventing, preempting, or disrupting terrorist attacks against the United States.
…
(U//FOUO) Attacks in Brussels Reaffirm ISIL’s Ability to Conduct Complex Attacks in Europe
(U//FOUO) DHS, FBI, and NCTC assess the 22 March 2016 attacks in Brussels, Belgium targeting Zaventem International Airport and the Brussels Metro system—for which the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) has claimed responsibility—demonstrate the group’s continued ability to conduct complex, coordinated attacks in Western Europe using multiple operatives and relatively simple tactics. We are not aware of any direct links to the Homeland; however, radicalized individuals inspired by ISIL operating alone or in small groups continue to have the ability to conduct relatively unsophisticated attacks with little to no warning in the United States.*
(U//FOUO) We judge the Brussels attackers probably conducted preoperational surveillance, did some level of tactical planning, and had familiarity with the targets prior to the attack, but may have expedited their plans after the arrest—several days prior in Belgium—of the sole surviving attacker involved in the November 2015 Paris attacks. We further assess the large amount of explosives used, willingness to operate despite well-publicized efforts by security officials to locate potential ISIL operatives, and the use of operational security to avoid law enforcement detection during the preoperational phase indicate some level of training. The attackers were part of an extensive support network and infrastructure in Belgium that also conducted the Paris attacks. This same network may have allowed the operatives to acquire materials and false documents, fabricate explosives, and may have facilitated connections with individuals based in Syria.
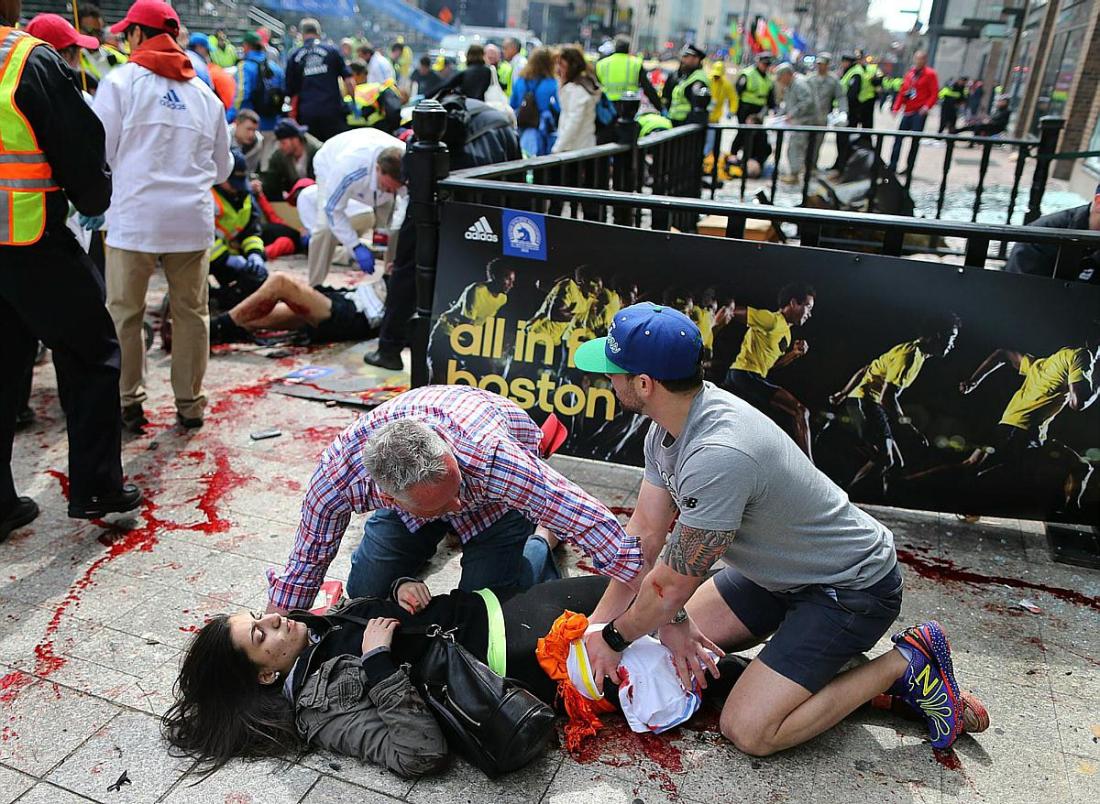
(U//FOUO) Attack Overview: On 22 March 2016, at least four and as many as five operatives divided into two teams that detonated homemade explosive devices estimated to contain between 30 and 60 pounds of triacetone triperoxide (TATP) at Brussels Zaventem International Airport and onboard a train in the Brussels subway, killing at least 32 and injuring over 300. Two operatives at the airport and one individual at the metro conducted suicide operations, which also resulted in over a dozen American casualties, including at least two deaths. Belgian authorities have arrested a man believed to be the third operative seen in CCTV footage at the airport and are investigating the possibility of an accomplice at the metro prior to the explosion.
(U) Airport Attack: At approximately 0758 local time, two improvised explosive devices (IEDs) believed to have been concealed in luggage detonated seconds apart in the passenger check-in area for several international airlines, including a US carrier. The attackers did not attempt to enter areas where their bags would be subject to security screening. Authorities later found a third viable device at the airport, which Belgian officials speculate might have been designed to target first responders, according to a statement from the Belgian federal prosecutor to the press. The device was later detonated by explosive ordnance disposal technicians. The third alleged operative at the airport was seen in security footage with the two suicide operatives in the moments prior to the attack, but he fled the scene and was arrested by Belgian authorities on 8 April.
(U) Subway Attack: Approximately 80 minutes after the airport explosions, at 0910 local time, an explosion occurred on a train as it departed the Maelbeek metro station, killing 13, according to the Brussels transit operator STIB. At least one operative, possibly aided by a second operative, entered the Maelbeek metro station and boarded the middle car of the three-car train, according to Belgian officials cited in media reporting., The blast occurred during morning rush hour near the European Union buildings, raising the possibility the operatives were targeting European government employees.
…
(U) Importance of Suspicious Activity Reporting
(U//FOUO) We encourage reporting of suspicious activity to appropriate authorities and encourage our homeland security, military, law enforcement, first responders, and private sector partners to remain vigilant. We face an increased challenge in detecting in-progress terrorist plots by individuals or small groups acting quickly and independently or with only tenuous ties to foreign handlers. Pre-operational indicators are likely to be difficult to detect; therefore, state, local, tribal, territorial, and private sector partners play a critical role in identifying and reporting suspicious activities and raising the awareness of federal counterterrorism officials.
(U//FOUO) The acquisition of materials for constructing an explosive device, a necessary stage in the execution of any IED attack, offers an opportunity for detection and disruption of plots. Thus, it is critical that point-of-sale employees understand how their products can be misused and are trained to recognize indicators of suspicious purchases and methods of reporting this information.
» (U//FOUO) In May 2015, a tip by a vigilant hardware store clerk to local police about a potentially suspicious purchase of an explosive precursor led German authorities to foil a possible attack against a major sporting event in the country after a couple purchased an unusually large amount of hydrogen peroxide. German authorities later discovered the couple presented fraudulent credentials and were associated with the local violent extremist community in Germany.
» (U//FOUO) The FBI arrested Saudi national Khalid Aldawsari in late February 2011 after he attempted to purchase a highly concentrated phenol solution—a precursor for the explosive trinitrophenol or picric acid—and raised suspicions of a freight company in Texas after the delivery of an unexpected package from a North Carolina chemical company. Aldawsari attempted to bypass the chemical company’s restriction on sending shipments to an individual or a residence, but he did not have permission from the freight company to have the package delivered. Aldawsari was sentenced to life in prison in June 2012 for attempted use of a weapon of mass destruction, according to a January 2014 FBI press release from the US Court of Appeals affirming his conviction.
Terrorism Definition, Terrorism In America, Terrorism Statistics, Terrorism News, Terrorism In Europe, Terrorism Meaning, Terrorism In The United States, Terrorism Facts, Terrorism In France, Terrorism Definition Fbi, Terrorism Articles, Terrorism Around The World, Terrorism And Homeland Security, Terrorism And Political Violence, Terrorism And Social Media, Terrorism Act, Terrorism And The Media, Terrorism And Religion, Terrorism Apush, Terrorism Alert Desk, Terrorism By Religion, Terrorism Before 9\/11, Terrorism Books, Terrorism By Country, Terrorism By Ideology, Terrorism By Race, Terrorism By Religion Statistics, Terrorism Background, Terrorism Before And After 9\/11, Terrorism Britain, Terrorism Current Events, Terrorism Causes, Terrorism Can Be Defined As, Terrorism Charges, Terrorism Coverage, Terrorism Cartoon, Terrorism Clipart, Terrorism Cnn, Terrorism Chart, Terrorism Conference 2017, Terrorism Definition, Terrorism Definition Fbi, Terrorism Def, Terrorism Deaths Per Year, Terrorism Database, Terrorism Defined, Terrorism Documentary, Terrorism Deaths In Us, Terrorism During Ramadan, Terrorism Definition Quizlet, Terrorism Examples, Terrorism Europe, Terrorism Essay, Terrorism Events, Terrorism Effects, Terrorism Etymology, Terrorism England, Terrorism Expert, Terrorism East Africa, Terrorism Explained, Terrorism Facts, Terrorism France, Terrorism Financing, Terrorism Fbi Definition, Terrorism Fbi, Terrorism Facts 2016, Terrorism Foreign Policy, Terrorism Fear, Terrorism Fox News, Terrorism From Above, Terrorist Groups, Terrorism Graph, Terrorism Germany, Terrorism Global Issue, Terrorism Greece, Terrorism Government Definition, Terrorism Globalization, Terrorism Great Britain, Terrorism Government, Terrorism Goal, Terrorism History, Terrorism Has No Religion, Terrorism Has Increased Job Opportunities In The, Terrorism Hotline, Terrorism Headlines, Terrorism Hot Spots, Terrorism Homeland Security, Terrorism How The West Can Win, Terrorism How To Respond, Terrorism Hate Crime, Terrorism In America, Terrorism In Europe, Terrorism In The United States, Terrorism In France, Terrorism In Russia, Terrorism In Africa, Terrorism In Japan, Terrorism In The Middle East, Terrorism In China, Terrorism In Italy, Terrorist Jokes, Terrorism Japan, Terrorism Journals, Terrorism Justified, Terrorism Jobs, Terrorism Jordan, Terrorism Justification, Terrorism Journal Articles, Terrorism June 2017, Terrorism Jihad And The Bible, Terrorism Knowledge Base, Terrorism Kenya, Terrorism Kkk, Terrorism Kidnapping And Hostage Taking, Terrorism Kyrgyzstan, Terrorism Kashmir, Terrorism Kidnapping, Terrorism Kuwait, Terrorist Keywords, Terrorism Quran, Terrorism London, Terrorism Legal Definition, Terrorism Liaison Officer, Terrorism Laws, Terrorism Lesson Plans, Terrorism List, Terrorism London 2017, Terrorism Law Definition, Terrorism Logo, Terrorism Levels, Terrorism Meaning, Terrorism Movies, Terrorism Map, Terrorist Meme, Terrorism Middle East, Terrorism Morocco, Terrorism Media, Terrorism Mental Illness, Terrorism Manchester, Terrorist Meaning, Terrorism News, Terrorism Nyc, Terrorism New York Times, Terrorism Now, Terrorism Nigeria, Terrorism Netherlands, Terrorism North Korea, Terrorism Norway, Terrorism Numbers, Terrorism Notes, Terrorism Origin, Terrorism On The Rise, Terrorism Over Time, Terrorism On Social Media, Terrorism On Us Soil, Terrorism On The Internet, Terrorism Original Definition, Terrorism Over The Years, Terrorism Objectives, Terrorism Online, Terrorism Prevention, Terrorism Political Cartoons, Terrorism Pictures, Terrorism Philippines, Terrorism Powerpoint, Terrorism Problems, Terrorism Psychology, Terrorism Policy, Terrorist Propaganda, Terrorism Prevention Act 2015, Terrorism Quotes, Terrorism Quizlet, Terrorism Questions, Terrorism Quiz, Terrorism Quran, Terrorism Qatar, Terrorism Quick Facts, Terrorism Quiz Questions, Terrorism Quotes Goodreads, Terrorism Qualifications, Terrorism Risk Insurance Act, Terrorism Refers To, Terrorism Research, Terrorism Research Paper, Terrorism Research Center, Terrorism Risk Insurance Program, Terrorism Rates, Terrorism Report, Terrorism Religion, Terrorism Russia, Terrorism Statistics, Terrorism Synonyms, Terrorism Statistics 2016, Terrorism Solutions, Terrorism Studies, Terrorism Statistics Us, Terrorism Since 9\/11, Terrorism Statistics 2017, Terrorism Sentence, Terrorism Spain, Terrorism Today, Terrorism Timeline, Terrorism Threat Levels, Terrorism Topics, Terrorism Task Force, Terrorism Types, Terrorism Threats, Terrorism Tracker, Terrorism Tactics, Terrorism Trends, Terrorism United States, Terrorism Uk, Terrorism Us Definition, Terrorism Us Code, Terrorism United Kingdom, Terrorism Un, Terrorism Unit, Terrorism Un Definition, Terrorism Us Statistics, Terrorism Us Law, Terrorism Video, Terrorism Vs War, Terrorism Vocabulary, Terrorism Vs Gun Violence, Terrorist Videos, Terrorism Victims, Terrorism Vs Freedom Fighter, Terrorism Violence, Terrorism Victims Fund, Terrorism Vs Extremism, Terrorism Wikipedia, Terrorism Worksheet, Terrorism Webquest, Terrorism Worldwide, Terrorism Webster, Terrorism War, Terrorist Watch List, Terrorism War And Bush, Terrorism Will Never End, Terrorism Warning, Terrorism Xinjiang, Terrorism Poll, Terrorism Xtc, Terrorism Xtc Lyrics, Xenophobia Terrorism, Xl Terrorism Insurance, Xkcd Terrorism, Xinjiang Terrorism, Xian Terrorism, Xinjiang Terrorism China, Terrorism Youtube, Terrorism Yesterday, Terrorism Yemen, Terrorist Yell, Terrorist Youtube, Terrorist Yelling Allahu Akbar, Terrorist Yee, Terrorist Your Game Is Through, Terrorist Yelling Allahu Akbar And Explodes, Terrorist Yahoo Answers, Terrorism Zimbabwe, Terrorism Zambia, Terrorism Zones Pool Re, Terrorism Zanzibar, Terrorism Zones Insurance, Terrorism Zeitgeist, Terrorism Zurich, Terrorism Zealots, Terrorism Zone C, Terrorism Zinn, Terrorism Definition, Terrorism In America, Terrorism Statistics, Terrorism News, Terrorism In Europe, Terrorism Meaning, Terrorism In The United States, Terrorism Facts, Terrorism In France, Terrorism Definition Fbi, Terrorism Articles, Terrorism Around The World, Terrorism And Homeland Security, Terrorism And Political Violence, Terrorism And Social Media, Terrorism Act, Terrorism And The Media, Terrorism And Religion, Terrorism Apush, Terrorism Alert Desk, Terrorism By Religion, Terrorism Before 9\/11, Terrorism Books, Terrorism By Country, Terrorism By Ideology, Terrorism By Race, Terrorism By Religion Statistics, Terrorism Background, Terrorism Before And After 9\/11, Terrorism Britain, Terrorism Current Events, Terrorism Causes, Terrorism Can Be Defined As, Terrorism Charges, Terrorism Coverage, Terrorism Cartoon, Terrorism Clipart, Terrorism Cnn, Terrorism Chart, Terrorism Conference 2017, Terrorism Definition, Terrorism Definition Fbi, Terrorism Def, Terrorism Deaths Per Year, Terrorism Database, Terrorism Defined, Terrorism Documentary, Terrorism Deaths In Us, Terrorism During Ramadan, Terrorism Definition Quizlet, Terrorism Examples, Terrorism Europe, Terrorism Essay, Terrorism Events, Terrorism Effects, Terrorism Etymology, Terrorism England, Terrorism Expert, Terrorism East Africa, Terrorism Explained, Terrorism Facts, Terrorism France, Terrorism Financing, Terrorism Fbi Definition, Terrorism Fbi, Terrorism Facts 2016, Terrorism Foreign Policy, Terrorism Fear, Terrorism Fox News, Terrorism From Above, Terrorist Groups, Terrorism Graph, Terrorism Germany, Terrorism Global Issue, Terrorism Greece, Terrorism Government Definition, Terrorism Globalization, Terrorism Great Britain, Terrorism Government, Terrorism Goal, Terrorism History, Terrorism Has No Religion, Terrorism Has Increased Job Opportunities In The, Terrorism Hotline, Terrorism Headlines, Terrorism Hot Spots, Terrorism Homeland Security, Terrorism How The West Can Win, Terrorism How To Respond, Terrorism Hate Crime, Terrorism In America, Terrorism In Europe, Terrorism In The United States, Terrorism In France, Terrorism In Russia, Terrorism In Africa, Terrorism In Japan, Terrorism In The Middle East, Terrorism In China, Terrorism In Italy, Terrorist Jokes, Terrorism Japan, Terrorism Journals, Terrorism Justified, Terrorism Jobs, Terrorism Jordan, Terrorism Justification, Terrorism Journal Articles, Terrorism June 2017, Terrorism Jihad And The Bible, Terrorism Knowledge Base, Terrorism Kenya, Terrorism Kkk, Terrorism Kidnapping And Hostage Taking, Terrorism Kyrgyzstan, Terrorism Kashmir, Terrorism Kidnapping, Terrorism Kuwait, Terrorist Keywords, Terrorism Quran, Terrorism London, Terrorism Legal Definition, Terrorism Liaison Officer, Terrorism Laws, Terrorism Lesson Plans, Terrorism List, Terrorism London 2017, Terrorism Law Definition, Terrorism Logo, Terrorism Levels, Terrorism Meaning, Terrorism Movies, Terrorism Map, Terrorist Meme, Terrorism Middle East, Terrorism Morocco, Terrorism Media, Terrorism Mental Illness, Terrorism Manchester, Terrorist Meaning, Terrorism News, Terrorism Nyc, Terrorism New York Times, Terrorism Now, Terrorism Nigeria, Terrorism Netherlands, Terrorism North Korea, Terrorism Norway, Terrorism Numbers, Terrorism Notes, Terrorism Origin, Terrorism On The Rise, Terrorism Over Time, Terrorism On Social Media, Terrorism On Us Soil, Terrorism On The Internet, Terrorism Original Definition, Terrorism Over The Years, Terrorism Objectives, Terrorism Online, Terrorism Prevention, Terrorism Political Cartoons, Terrorism Pictures, Terrorism Philippines, Terrorism Powerpoint, Terrorism Problems, Terrorism Psychology, Terrorism Policy, Terrorist Propaganda, Terrorism Prevention Act 2015, Terrorism Quotes, Terrorism Quizlet, Terrorism Questions, Terrorism Quiz, Terrorism Quran, Terrorism Qatar, Terrorism Quick Facts, Terrorism Quiz Questions, Terrorism Quotes Goodreads, Terrorism Qualifications, Terrorism Risk Insurance Act, Terrorism Refers To, Terrorism Research, Terrorism Research Paper, Terrorism Research Center, Terrorism Risk Insurance Program, Terrorism Rates, Terrorism Report, Terrorism Religion, Terrorism Russia, Terrorism Statistics, Terrorism Synonyms, Terrorism Statistics 2016, Terrorism Solutions, Terrorism Studies, Terrorism Statistics Us, Terrorism Since 9\/11, Terrorism Statistics 2017, Terrorism Sentence, Terrorism Spain, Terrorism Today, Terrorism Timeline, Terrorism Threat Levels, Terrorism Topics, Terrorism Task Force, Terrorism Types, Terrorism Threats, Terrorism Tracker, Terrorism Tactics, Terrorism Trends, Terrorism United States, Terrorism Uk, Terrorism Us Definition, Terrorism Us Code, Terrorism United Kingdom, Terrorism Un, Terrorism Unit, Terrorism Un Definition, Terrorism Us Statistics, Terrorism Us Law, Terrorism Video, Terrorism Vs War, Terrorism Vocabulary, Terrorism Vs Gun Violence, Terrorist Videos, Terrorism Victims, Terrorism Vs Freedom Fighter, Terrorism Violence, Terrorism Victims Fund, Terrorism Vs Extremism, Terrorism Wikipedia, Terrorism Worksheet, Terrorism Webquest, Terrorism Worldwide, Terrorism Webster, Terrorism War, Terrorist Watch List, Terrorism War And Bush, Terrorism Will Never End, Terrorism Warning, Terrorism Xinjiang, Terrorism Poll, Terrorism Xtc, Terrorism Xtc Lyrics, Xenophobia Terrorism, Xl Terrorism Insurance, Xkcd Terrorism, Xinjiang Terrorism, Xian Terrorism, Xinjiang Terrorism China, Terrorism Youtube, Terrorism Yesterday, Terrorism Yemen, Terrorist Yell, Terrorist Youtube, Terrorist Yelling Allahu Akbar, Terrorist Yee, Terrorist Your Game Is Through, Terrorist Yelling Allahu Akbar And Explodes, Terrorist Yahoo Answers, Terrorism Zimbabwe, Terrorism Zambia, Terrorism Zones Pool Re, Terrorism Zanzibar, Terrorism Zones Insurance, Terrorism Zeitgeist, Terrorism Zurich, Terrorism Zealots, Terrorism Zone C, Terrorism Zinn, Dhs Office, Dhs Michigan, Dhs Phone Number, Dhs Link, Dhs Live, Dhs Near Me, Dhs To Usd, Dhs Office Locator, Dhs Skokie, Dhs Child Care, Dhs Application, Dhs Adrian Mi, Dhs Assistance, Dhs Authorization, Dhs Application Online, Dhs Address, Dhs Apply Online, Dhs Allegan Mi, Dhs Ann Arbor, Dhs Apply, Dhs Battle Creek Mi, Dhs Bay City Mi, Dhs Billing, Dhs Building, Dhs Bridge Card, Dhs Benefits, Dhs Battle Creek Michigan, Dhs Big Rapids, Dhs Baldwin Mi, Dhs Background Check Michigan, Dhs Child Care, Dhs Clearance, Dhs Champs, Dhs Child Care Provider, Dhs Caseworker Lookup, Dhs Clio Rd, Dhs Caro Mi, Dhs Clio Road, Dhs Customer Service, Dhs Conner, Dhs Detroit, Dhs Daycare, Dhs Dearborn, Dhs Diecast, Dhs Directory, Dhs Department, Dhs Daycare Help, Dhs Disability, Dhs Dental, Dhs Definition, Dhs Emergency, Mdhhs Ems, Dhs Employment Verification Form, Mdhhs Email, Dhs Emergency Services, Dhs Email Address, Mdhhs Employee Directory, Dhs Equipment, Dhs Employment, Dhs Ebt, Dhs Flint Mi, Dhs Food Stamps, Dhs Flint, Dhs Forms, Dhs Fax Number, Dhs Fast, Dhs Food Assistance, Dhs Form 3200, Dhs Flint Michigan Clio Road, Dhs Form 3503, Dhs Greydale, Dhs Grand Rapids, Dhs Grand River Warren, Dhs Genesee County, Dhs Gladwin Mi, Dhs Greenfield, Dhs Gratiot 7 Mile, Dhs Gr Mi, Dhs Greenfield Joy, Dhs Gaylord Mi, Dhs Hours, Dhs Howell Mi, Dhs Holland Mi, Dhs Hillsdale Mi, Dhs Hartford Mi, Dhs Harrison Mi, Dhs Holland, Dhs Hastings Mi, Dhs Hart Mi, Dhs Home Health Care, Dhs Inkster, Dhs Ib Bio, Dhs In Pontiac Mi, Dhs Ibilling, Dhs In Lansing, Dhs In Detroit, Dhs In Redford Mi, Dhs In Michigan, Dhs In Taylor, Dhs Illinois, Dhs Jobs, Dhs Jackson Mi, Dhs Jobs In Michigan, Dhs Joy Road And Greenfield, Dhs Joy Rd, Dhs Joy, Dhs Job Opportunities, Dhs Jobs Mi, Dhs Job Openings, Dhs Jay Ok, Dhs Kalamazoo Mi, Dhs Kent County, Dhs Kalkaska, Dhs Kelly, Dhs Kalamazoo Login, Dhs Key Club, Dhs Klamath Falls Oregon, Dhs Knoxville, Dhs Kansas, Dhs Kentucky, Dhs Login, Dhs Lansing Mi, Dhs Lapeer Mi, Dhs Lansing Michigan, Dhs Locations, Dhs Lappin, Dhs Live, Dhs Logo, Dhs Lappin And Gratiot, Dhs Lansing Fax Number, Dhs Michigan, Dhs Management, Dhs Monroe Mi, Dhs Macomb, Dhs Medicaid, Dhs Muskegon Mi, Dhs Midland Mi, Dhs Main Office, Dhs Mt Clemens, Dhs Monroe Michigan, Dhs Near Me, Dhs Number, Dhs Number Lansing Mi, Dhs Novi Mi, Dhs Number On Lappin, Dhs News, Dhs New Hire Form, Dhs Novi, Dhs Near Me Hours, Dhs Nhs, Dhs Office, Dhs Oakland County, Dhs Office Detroit, Dhs Oregon, Dhs Okc, Dhs Online, Dhs Office Pontiac Mi, Dhs Office On Conners, Dhs Office On Lappin, Dhs Office On Plymouth, Dhs Phone Number, Dhs Pontiac, Dhs Port Huron Mi, Dhs Port Huron Michigan, Dhs Provider Login, Dhs Provider Payment Schedule 2017, Dhs Payment Dates 2017, Dhs Plymouth, Dhs Provider, Dhs Police, Dhs Questions, Dhs Questionnaire, Dhs Quincy Illinois, Dhs Quote, Dhs Questions And Answers, Dhs Qmb Program, Dhs Qhsr, Dhs Questionnaire Pdf, Dhs Quarterly Reports, Dhs Quincy, Dhs Rent Assistance, Dhs Redford, Dhs Royal Oak, Dhs Redetermination Application Michigan, Dhs Rochester Hills Mi, Dhs Ri, Dhs Reed City Mi, Dhs Royal Oak Mi, Dhs Rogers City Mi, Dhs Redetermination Form Medical, Dhs Sign In, Dhs Shampoo, Dhs Sandusky Mi, Dhs Ser, Dhs Saginaw Mi, Dhs Stanton Mi, Dhs Secretary, Dhs Services, Dhs Sterling Heights, Dhs Southfield Mi, Dhs Taylor Mi, Dhs To Usd, Mdhhs Training, Mdhhs Taylor, Dhs Traverse City, Dhs Twitter, Dhs Trip, Mdhhs Tb, Mdhhs Twitter, Mdhhs Third Party Liability, Dhs Union St, Dhs Unemployment, Dhs Unearned Income Notice, Dhs Uscis, Dhs Usa, Dhs Uscis Login, Dhs Uniform, Dhs Utah, Dhs Utility Assistance Michigan, Dhs Uscis Genealogy, Dhs Van Buren, Dhs Verification Of Assets, Dhs Van Dyke, Dhs Verification In Process, Dhs Vinelink, Dhs Verification Of Employment, Dhs Vine, Dhs Voice, Dhs Virginia, Dhs Va 20598, Dhs Website, Dhs Warren, Dhs Washtenaw County, Dhs Wayne County, Dhs Worker, Dhs Warren And Conner, Dhs Warren And Grand River, Dhs Wayne County Mi, Dhs Wayne County Number, Dhs Wic, Dhs X6006, Dhs Xc, Dhs X4002, Dhs X6002, Dhs X3002, Dhs X6007, Dhs X6006 Review, Dhs X Ray, Dhs X3002 Review, Dhs X5002, Dhs Ypsilanti Mi Hours, Dhs Ypsilanti Michigan, Dhs Ypsi, Dhs Ypsilanti, Dhs Ypsilanti Mi, Dhs Ypsilanti Hours, Dhs Yearbook, Dhs Yellville Ar, Dhs Youtube, Dhs Ypsilanti Mi Phone Number, Dhs Zinc Shampoo, Dhs Zinc Shampoo Walgreens, Dhs Zinc, Dhs Zinc Shampoo 16 Oz, Dhs Zinc Shampoo Target, Dhs Zinc Shampoo Cvs, Dhs Zinc Shampoo Review, Dhs Zip Code, Dhs Zambia, Dhs Zinc Body Wash, Fbi Most Wanted, Fbi Jobs, Fbi Director, Fbi Salary, Fbi Agent, Fbi Background Check, Fbi Agent Salary, Fbi Headquarters, Fbi Special Agent, Fbi Internships, Fbi Agent, Fbi Agent Salary, Fbi Academy, Fbi Application, Fbi Analyst, Fbi Atlanta, Fbi Agent Jobs, Fbi Anon, Fbi Address, Fbi Arrests, Fbi Background Check, Fbi Badge, Fbi Bau, Fbi Building, Fbi Boston, Fbi Bap, Fbi Baltimore, Fbi Benefits, Fbi Budget, Fbi Building Dc, Fbi Careers, Fbi Crime Statistics, Fbi Clearance, Fbi Criminal Background Check, Fbi Chicago, Fbi Citizens Academy, Fbi Crime Statistics By Race, Fbi Contact, Fbi Channeler, Fbi Candidates, Fbi Director, Fbi Director Candidates, Fbi Director James Comey, Fbi Definition, Fbi Director Fired, Fbi Director Salary, Fbi Definition Of Terrorism, Fbi Database, Fbi Dallas, Fbi Drug Policy, Fbi Employment, Fbi Email Address, Fbi Employment Drug Policy, Fbi El Paso, Fbi Employees, Fbi Emblem, Fbi Established, Fbi Education Center, Fbi Education, Fbi Executive Branch, Fbi Fingerprinting, Fbi Files, Fbi Field Offices, Fbi Fingerprint Card, Fbi Fitness Test, Fbi Facebook, Fbi Fingerprint Check, Fbi Forensic Accountant, Fbi Foia, Fbi Founder, Fbi Glock, Fbi Games, Fbi Gov, Fbi Glassdoor, Fbi Guns, Fbi Gang List, Fbi Gun Statistics, Fbi Gif, Fbi Gift Shop, Fbi General Counsel, Fbi Headquarters, Fbi Hrt, Fbi History, Fbi Houston, Fbi Hiring, Fbi Hate Crime Statistics, Fbi Head, Fbi Hat, Fbi Honors Internship, Fbi Hotline, Fbi Internships, Fbi Investigation, Fbi Intelligence Analyst, Fbi Informant, Fbi Irt, Fbi Investigation Trump, Fbi Ic3, Fbi Infragard, Fbi Internet Fraud, Fbi Id, Fbi Jobs, Fbi Jacket, Fbi James Comey, Fbi Jurisdiction, Fbi Job Description, Fbi Jobs Apply, Fbi Jacksonville, Fbi Jade Helm, Fbi Jobs Chicago, Fbi Jackson Ms, Fbi Kansas City, Fbi Kids, Fbi Knoxville, Fbi Kidnapping, Fbi Komi, Fbi Kentucky, Fbi Killed Jfk, Fbi Kkk, Fbi Kodi, Fbi K9 Unit, Fbi Logo, Fbi Leeda, Fbi Los Angeles, Fbi Locations, Fbi Las Vegas, Fbi Leaks, Fbi Leader, Fbi Linguist, Fbi Louisville, Fbi Login, Fbi Most Wanted, Fbi Most Wanted List, Fbi Meaning, Fbi Meme, Fbi Movies, Fbi Museum, Fbi Motto, Fbi Miami, Fbi Mission Statement, Fbi Most Dangerous Cities, Fbi Number, Fbi News, Fbi National Academy, Fbi Nics, Fbi New York, Fbi New Orleans, Fbi Newark, Fbi New York Tv Show, Fbi Near Me, Fbi Nominee, Fbi Offices, Fbi Org Chart, Fbi Omaha, Fbi Operative, Fbi On Trump, Fbi Organizational Chart, Fbi Obama Meme, Fbi Obama, Fbi Oklahoma City, Fbi Office Near Me, Fbi Phone Number, Fbi Profiler, Fbi Pft, Fbi Police, Fbi Pay Scale, Fbi Phoenix, Fbi Pay, Fbi Philadelphia, Fbi Positions, Fbi Pittsburgh, Fbi Quantico, Fbi Qualifications, Fbi Q Target, Fbi Quotes, Fbi Quiz, Fbi Questions, Fbi Qr Code, Fbi Qas, Fbi Quantico Address, Fbi Quantico Tours, Fbi Requirements, Fbi Russia, Fbi Russia Investigation, Fbi Report, Fbi Ranks, Fbi Recruiting, Fbi Raid, Fbi Records, Fbi Rape Statistics, Fbi Russia Trump, Fbi Salary, Fbi Special Agent, Fbi Stands For, Fbi Swat, Fbi Special Agent Salary, Fbi Surveillance, Fbi Statistics, Fbi Sos, Fbi Surveillance Van, Fbi Seal, Fbi Training, Fbi Top Ten, Fbi Trump, Fbi Trump Russia, Fbi Tip Line, Fbi Tv Shows, Fbi Twitter, Fbi Tips, Fbi Teen Academy, Fbi Tours, Fbi Ucr, Fbi Ucr 2016, Fbi Units, Fbi Ucr 2015, Fbi Undercover, Fbi Unsolved Cases, Fbi Upin, Fbi Utah, Fbi Usa, Fbi Uniforms, Fbi Vs Cia, Fbi Vault, Fbi Virus, Fbi Vs Apple, Fbi Virtual Academy, Fbi Vehicles, Fbi Violent Crime Statistics, Fbi Virginia, Fbi Van, Fbi Van Wifi, Fbi Website, Fbi Warning, Fbi Wiki, Fbi Wanted List, Fbi Watch List, Fbi Windbreaker, Fbi Warning Screen, Fbi White Collar Crime, Fbi Warrant Search, Fbi Weapons, Fbi X Files, Fbi Xl2, Fbi Xl31, Fbi Xl4, Fbi Xl2 Programming, Fbi Xl-31 Troubleshooting, Fbi Xl 31 Installation Manual, Fbi X Files Real, Fbi Xl2t Installation Manual, Fbi Xl 1215, Fbi Yearly Salary, Fbi Youtube, Fbi Youth Academy, Fbi Youth Leadership Academy, Fbi Yellow Brick Road, Fbi Youth Programs, Fbi Yearly Budget, Fbi Youth Leadership Academy Portland, Fbi Youngstown Ohio, Fbi Yearly Income, Fbi Zodiac Killer, Fbi Zodiac, Fbi Zip Code, Fbi Zodiac Killer List, Fbi Zero Files, Fbi Zodiac List, Fbi Zodiac Signs Killer, Fbi Zhang Yingying, Fbi Zion, Fbi Zodiac Crimes, Isis News, Isis Flag, Isis Thrown Off Cliff, Isis Goddess, Isis Definition, Isis Attack, Isis Uf, Isis Memes, Isis Map, Isis Website, Isis Attack, Isis Aspen, Isis And Osiris, Isis Archer, Isis Acronym, Isis Attacks In Us, Isis Asheville, Isis Antm, Isis Afghanistan, Isis Atrocities, Isis Band, Isis Bombing, Isis Build, Isis Beliefs, Isis Button, Isis Brown Sugar, Isis Books, Isis Being Killed, Isis Behind The Mask, Isis Best Gore, Isis Control Map, Isis Capital, Isis Chemical Weapons, Isis Caliphate, Isis Chan, Isis Cartoon, Isis Controlled Territory, Isis Candy Tomato, Isis Cnn, Isis Collection, Isis Definition, Isis Defeated, Isis Drones, Isis Documentary, Isis Death Toll, Isis Dead, Isis Deaths, Isis Daesh, Isis Drone Video, Isis Dc, Isis Egypt, Isis Explained, Isis Edc, Isis Europe, Isis Events, Isis Exhaust, Isis Enemies, Isis Excussion, Isis Exchange, Isis England, Isis Flag, Isis Fighters Killed, Isis Fighters Thrown Off Cliff, Isis Facts, Isis Fighters, Isis Fighters Executed, Isis Fails, Isis Funding, Isis Founder, Isis Flag For Sale, Isis Goddess, Isis Gallardo, Isis Goals, Isis Genocide, Isis Getting Shot, Isis Goat Meme, Isis Group, Isis Getting Bombed, Isis Goat, Isis Gif, Isis Harambe, Isis History, Isis Hair, Isis Hit List, Isis Heavy, Isis Hunting Permit, Isis Hostages, Isis Hunting, Isis Hand Sign, Isis Horus, Isis In Syria, Isis Iowa, Isis In The Philippines, Isis Iraq, Isis In Afghanistan, Isis In America, Isis Israel, Isis Ideology, Isis In Libya, Isis In Mosul, Isis Jokes, Isis Jhu, Isis Jv Team, Isis Jones, Isis Journal, Isis Jordan, Isis Jihad, Isis Japan, Isis John, Isis Joust Build, Isis King, Isis K, Isis Kids, Isis Kidnapping, Isis Knot, Isis Keyshia Wig, Isis Kurds, Isis Kneading, Isis Ksu, Isis King Engaged, Isis Leader, Isis Live Map, Isis Logo, Isis Leader Dead, Isis Location, Isis Las Vegas, Isis Losing, Isis Libya, Isis Lyrics, Isis Leadership, Isis Meaning, Isis Memes, Isis Map, Isis Mosul, Isis Magazine, Isis Music, Isis Members, Isis Mythology, Isis Marawi, Isis Music Hall, Isis News, Isis Name Meaning, Isis Name, Isis Numbers, Isis Net Worth, Isis News Mosul, Isis News Today, Isis National Anthem, Isis Nitric Acid Video, Isis New York, Isis Or Isil, Isis Origin, Isis Oasis, Isis Osiris, Isis Oil, Isis Oceanic, Isis Oracle, Isis On Twitter, Isis Osiris Horus, Isis Ohsu, Isis Propaganda, Isis Papers, Isis Pharmaceuticals, Isis Philippines, Isis Persona 5, Isis Pictures, Isis Phone Number, Isis Population, Isis Pizza, Isis Paris Attack, Isis Quotes, Isis Queen, Isis Quizlet, Isis Quran, Isis Questions, Isis Quartz, Isis Qaraqosh, Isis Quick Facts, Isis Qatar, Isis Quotes To America, Isis Religion, Isis Recruitment, Isis Recruitment Video, Isis Raqqa, Isis Romero, Isis Rea Boykin, Isis Russia, Isis Ramadan, Isis Reddit, Isis Recent Attacks, Isis Stands For, Isis Syria, Isis Symbol, Isis Song, Isis Sunni, Isis Social Media, Isis Shotgun, Isis Soldiers, Isis Smite, Isis Stronghold, Isis Thrown Off Cliff, Isis Territory, Isis Thrown Off Building Video, Isis Twitter, Isis Tv Show, Isis Theme Song, Isis Terrorist Attacks, Isis Torture, Isis Terrorist, Isis The Goddess, Isis Uf, Isis Uiowa, Isis Unveiled, Isis Uark, Isis Update, Isis Uk, Isis Using Drones, Isis Us, Isis Uniforms, Isis Urban Dictionary, Isis Vs Isil, Isis Valverde, Isis Victims, Isis Vs Usa, Isis Vegas, Isis Vs Taliban, Isis Vasconcellos, Isis Vs Kkk, Isis Vehicles, Isis Violence, Isis Website, Isis Wiki, Isis Wigs, Isis War, Isis Wings, Isis Women, Isis Wallet, Isis Weapons, Isis Waswas, Isis Wenger, Isis X Clan, Isis Xinjiang, Isis Xl, Isis Xpad, Isis X Rite, Isis Xinjiang China, Isis Xenophobia, Isis Xbox, Isis Youtube, Isis Yemen, Isis Yazidi, Isis Yugioh, Isis Youtube Channel, Isis Young, Isis Youth, Isis Youtube Ads, Isis Year Founded, Isis Y Osiris, Isis Zionist Plot, Isis Zoo, Isis Zion, Isis Zodiac, Isis Zone Of Control, Isis Zakat, Isis Zerocensorship, Isis Zodiac Sign, Isis Zarai Sandoval, Isis Zims, https://berndpulch.org/category/eev/


























































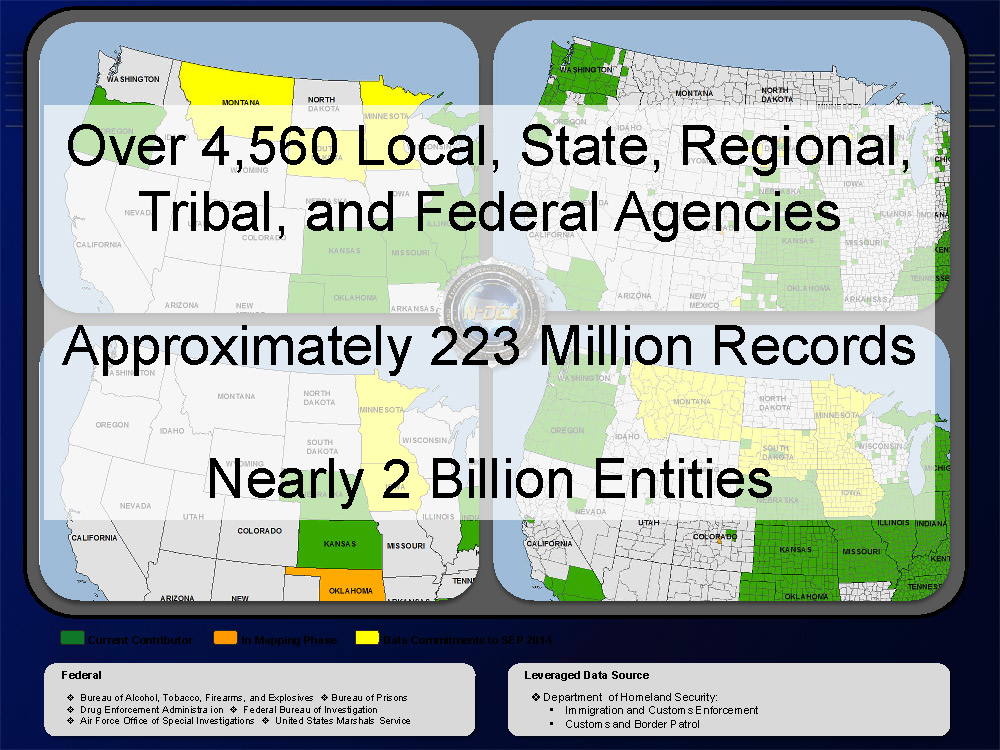
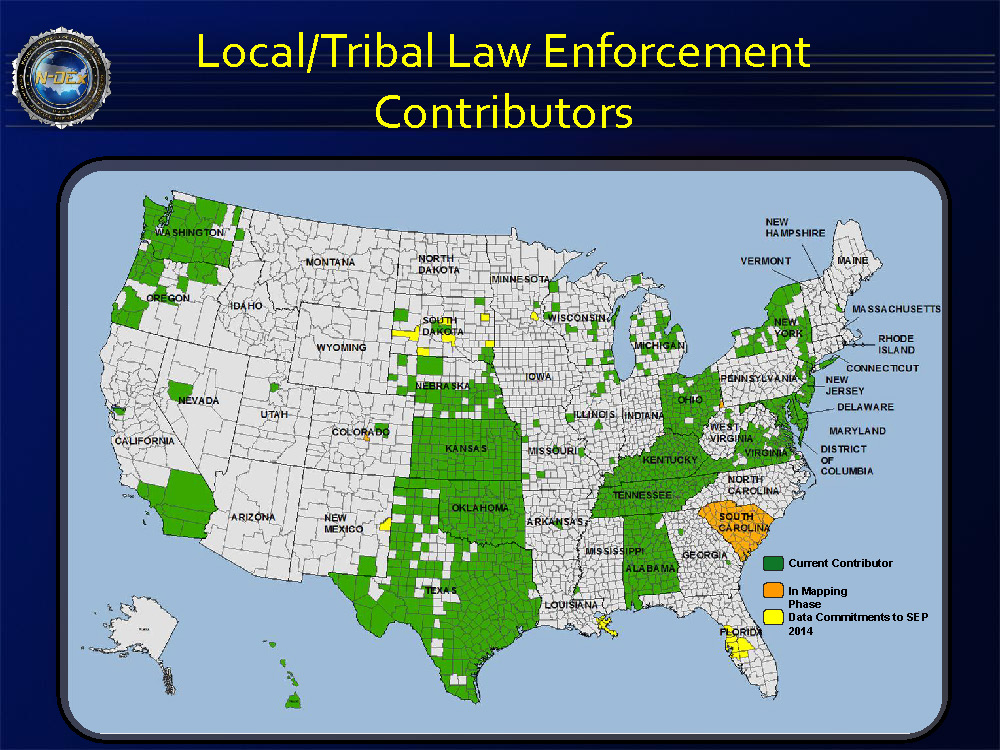
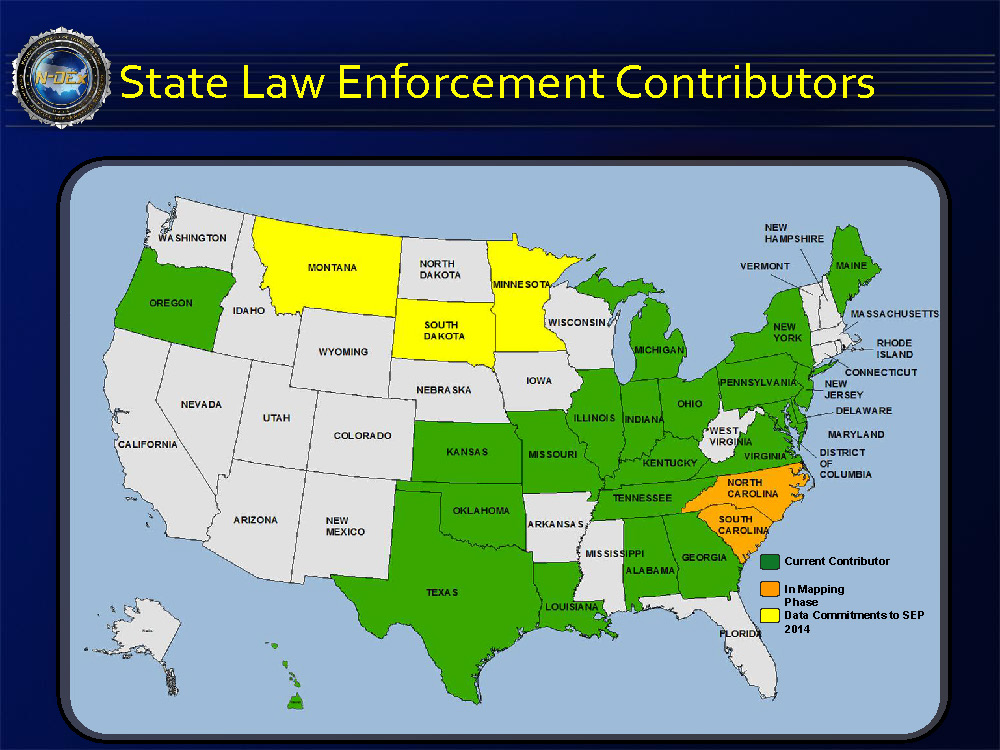
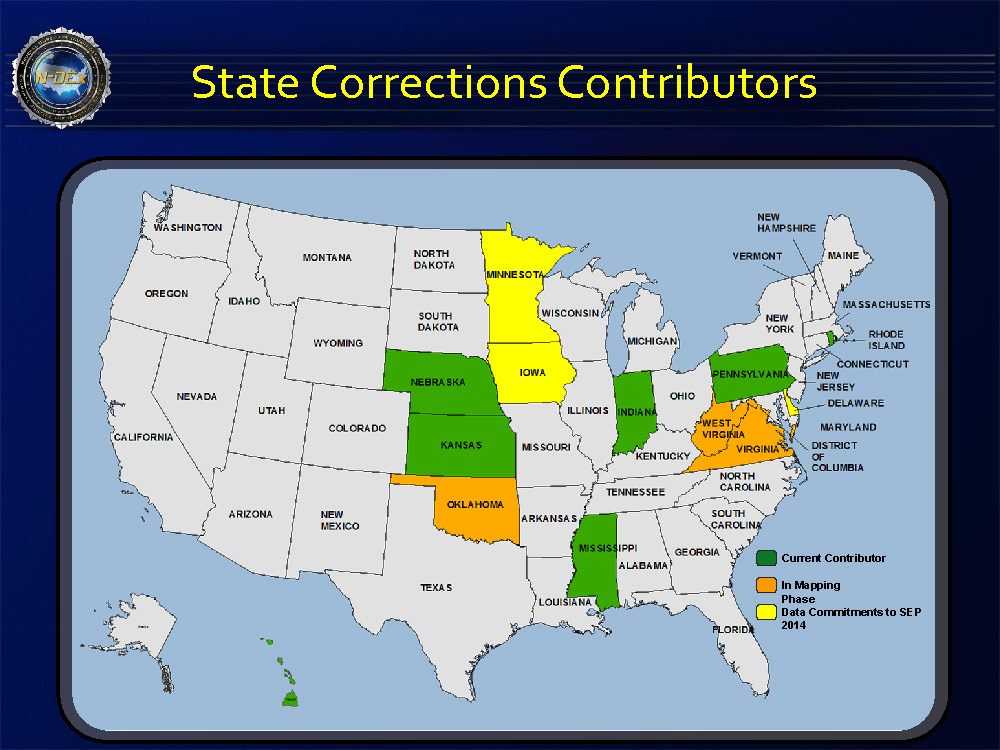


















 An Oregon man recently pled guilty to operating an unlicensed money transmittal business that illegally moved more than $172 million in and out of the United States.
An Oregon man recently pled guilty to operating an unlicensed money transmittal business that illegally moved more than $172 million in and out of the United States. 
You must be logged in to post a comment.